Services
OUR SERVICES
Explore Our Main Services
Agricultural biotechnology is a range of tools, including traditional breeding techniques, that alter living organisms, or parts of organisms, to make or modify products; improve plants or animals; or develop microorganisms for specific agricultural uses.
Algal biotechnology is a technology developed using algae.this can be further divided into microalgae technology and macroalgae technology.
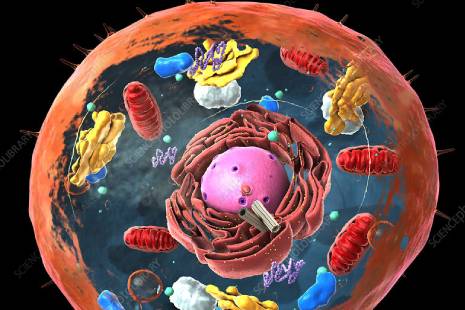
Animal cells are typical of the eukaryotic cell, enclosed by a plasma membrane and containing a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles.
Biochemistry is both life science and a chemical science - it explores the chemistry of living organisms and the molecular basis for the changes occurring in living cells.
Bioinformatics is a subdiscipline of biology and computer science concerned with the acquisition, storage, analysis, and dissemination of biological data, most often DNA and amino acid sequences.
The Cancer Biology portion of the site contains in-depth information about the structure and function of normal cells and cancer cells.
Cells are the basic building blocks of life. Bacteria consist of a single cell, while plants and animals are made of multiple types of cell.
Environmental biotechnology in particular is the application of processes for the protection and restoration of the quality of the environment
Enzyme technology encompasses modification of enzyme structure or its catalytic function to yield novel metabolites or to take part in new reaction pathways.
Food biotechnology is the use of technology to modify the genes of our food sources. Our food sources are animals, plants, and microorganisms
Marine biotechnology is a knowledge generation and conversion process: it unlocks access to biological compounds and provides novel uses for them.
Molecular biology is the study of biology at a molecular level. The field overlaps with other areas of biology and chemistry, particularly genetics and biochemistry.
Nanotechnology is science, engineering, and technology conducted at the nanoscale, which is about 1 to 100 nanometers.
Pharmacology is the study of how a drug affects a biological system and how the body responds to the drug.
Stem cell technology is a rapidly developing field that combines the efforts of cell biologists, geneticists, and clinicians and offers hope of effective treatment for a variety of malignant and non-malignant diseases.
The goal of tissue engineering is to assemble functional constructs that restore, maintain, or improve damaged tissues or whole organs.